Class Inheritance
Introduction:
- We will cover the following basic concepts:
- Understand the basics of Class Inheritance.
- Simple example class to understand how we can work with Class Inheritance in different scenarios.
- We will see the use of SUPER and ME keywords in the context of Inheritance.
- Create a program to demonstrate the different ways to call methods using Inheritance.
- Why Class Inheritance?
Lets Start
1. Let us create the below comparison chart to understand the basics of CLASS INHERITANCE.
2. Lets us create a simple eclipse class and make it work for different scenarios.
- We will add one method in each visibility section of the Eclipse Class as shown below.
- PUBLIC_METHOD, PROTECTED_METHOD, and PRIVATE METHOD.
- Now let us create the implementations for the created methods.
- Here we have created a FINAL CLASS ( i.e. add the FINAL keyword in the definition section of the class) just to see what happens if we try to Inherit a final class.
- Next let us create a class with the keyword INHERITING FROM ZCLASS_INHERITANCE.
- So now we can call ZCLASS_INHERITANCE SUPER CLASS & ZCLASS_SUB_INHERITANCE SUBCLASS.
- But there is some problem, as we can see below class ZCLASS_INHERITANCE is the FINAL CLASS and cannot have any subclass.
- In other words, ZCLASS_INHERITANCE cannot be inherited by other classes.

- Let us remove the FINAL keyword from the class ZCLASS_INHERITANCE.
- Now we can inherit the above class and create ZCLASS_SUB_INHERITANCE class.
- We will add one method in each visibility section of the SUBCLASS as shown below, just like the SUPER CLASS
- Create methods like PUBLIC_METHOD, PROTECTED_METHOD, and PRIVATE_METHOD.
- Interestingly, as we can see PUBLIC_METHOD & PROTECTTED_METHOD show errors as "METHOD was already declared" as shown below.
- This happens because the above methods have already been declared in SUPER CLASS and SUBCLASS ZCLASS_SUB_INHERITANCE is inherited from the CLASS ZCLASS_INHERITANCE.
- And yes, there is a way to use the same methods in the SUBCLASS.
 |
| Public method Error |
- We will use the keyword REDEFINITION.
- This keyword is to reuse the same methods from SUPER Class.
- As shown below we have redefined both PUBLIC_METHOD and PROTECTED_METHOD of the superclass to RE-IMPLEMENT ( OVERRIDE ) them in the subclass.
 |
| Sub Class Definition |
3. Let us now create some example methods using SUPER and ME keywords.
 |
| Sub Class Implementation |
- Now let us create the implementation of the redefined public method.
- PUBLIC_METHOD :
- Line 17: Here we have a simple WRITE statement.
- Line 19:
- There is an interesting keyword here named SUPER here.
- This keyword refers to objects of the superclass.
- That means when we call SUPER->PUBLIC_METHOD the public method of the superclass gets called.
- PROTECTED_METHOD:
- Line 22:
- Similar to the public method, we will call SUPER->PROTECTED_METHOD.
- We know from our study of Class Visibility, we can call the components of the superclass with PUBLIC & PROTECTED visibility from the Subclass.
- PRIVATE_METHOD:
- Line 25:
- If we observe the method PRIVATE_METHOD, which is part of the private section of both the SUPER and SUB Classes.
- Because the method belongs to the superclass's private section, we cannot redefine it in the subclass.
- This shows the PRIVATE SECTION is not affected by INHERITANCE.
- Now let us explore another way of calling the superclass method with the below example.
- Let us go back to the superclass and create the new method SUPER_PUBLIC_METHOD in PUBLIC_SECTION.
- Create the Implementation of the method as shown below.
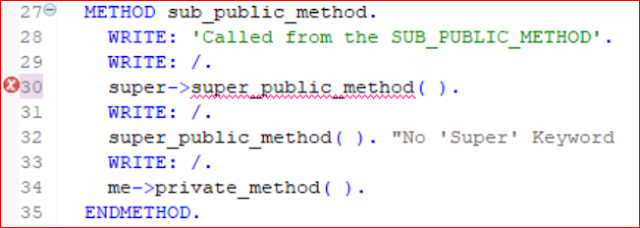
- Now Let us create the SUB_PUBIC_METHOD in the Public Section of the subclass.
- Line30:
- Let us call the method SUPER->SUPER_PUBLIC_METHOD in the implementation of the subclass method as shown below.
- We get an error stating that we can use the "SUPER keyword to call a superclass method only to call the previous implementation of the same method".
- For Example: refer to PUBLIC_METHOD and PROTECTED_METHOD implementation of the subclass.
- So how do we call the SUPER_PUBLIC_METHOD without redefining it in the Sub Class.
- Line 32:
- We simply do not use the SUPER keyword and we directly call it.
- LINE34:
- We will call the method PRIVATE_METHOD of the same class using ME as a self-reference parameter.
- SUPER: Reference to the objects of the superclass.
- ME: Local Self Reference to subclass.
4. Now let us run these scenarios in an example program.
- First, we will just call the public methods of the superclass directly from the created object of the superclass ZCLASS_INHERITANCE as all the methods in our example are INSTANCE METHODS.
- We will see the Program code on the LEFT-HAND SIDE of the Screenshot.
- And on the RIGHT-HAND SIDE of the screenshot, the ABAP CONSOLE displays the output of the ECLIPSE Program.
- Now let us call the methods of the superclass from the objects created for the subclass ZCLASS_SUB_INHERITANCE.
- Subclass had direct access to call the public method of the superclass as shown below.
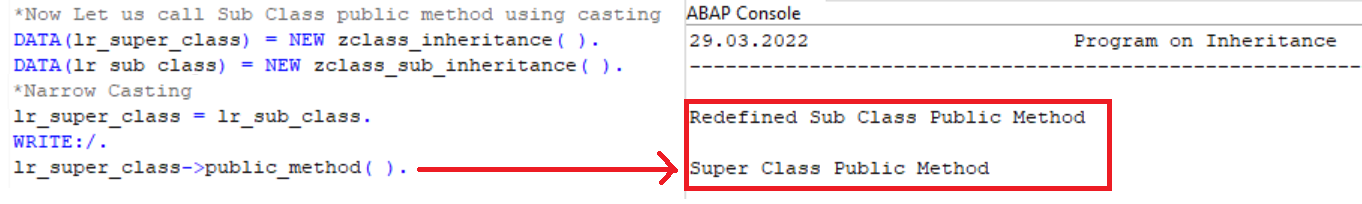
- Now let us call the subclass method from the superclass object.
- For that we need to do a "Narrowing Caste" or "Up Cast".
- LR_SUPER_CLASS = LR_SUB_CLASS : Will assign the reference of the subclass to superclass.
- This makes the superclass access components of the subclass.
- We will learn more about this in follow-up posts.
- Now let us call the superclass method from the subclass object using casting.
- For that we need to do a "Widening Cast" or "Down Cast".
- LR_SUB_CLASS ?= LR_SUPER_CLASS: Will assign the reference of the subclass to the superclass using ( ?= ) Cast Operator.
- Wait but this by itself doesn't work, the following error occurs.
5. So why do we need Inheritance?
- As we have discussed above, we can re-use the components of the superclass in the subclass with class visibility PUBLIC & PROTECTED.
- We can think of Inheritance as Extending the Super Class properties in the Sub Class and adding more required logic to the existing class components.
- This means inheritance can be super helpful in code reusability if a developer decides to use the existing functionality of a class along with some added functionality that is more specific to a requirement.
- We can OVERRIDE a method functionality in the subclass by REDEFINING them, which gives multiple functionalities to the same method, for EXAMPLE, PUBLIC_METHOD in our case.
- We can call this facility POLYMORPHISM in Object Oriented.
- Even INTERFACES help us with POLYMORPHISM but in a different way if compared with CLASS INHERITANCE. We will explore this topic later.
Example Code to Explore more:
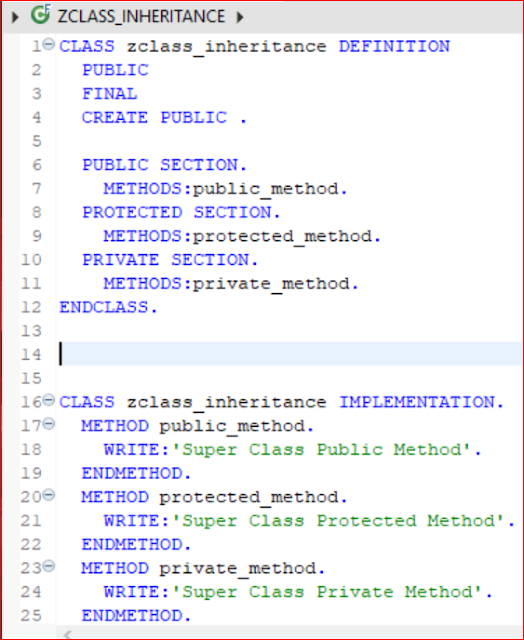
CLASS zclass_inheritance DEFINITION
PUBLIC
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
METHODS:public_method.
METHODS:super_public_method.
PROTECTED SECTION.
METHODS:protected_method.
PRIVATE SECTION.
METHODS:private_method.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS zclass_inheritance IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD public_method.
WRITE:'Super Class Public Method'.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD protected_method.
WRITE:'Super Class Protected Method'.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD private_method.
WRITE:'Super Class Private Method'.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD:super_public_method.
write:'Only Super Class Public Method'.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
Sub Class:
CLASS zclass_sub_inheritance DEFINITION
PUBLIC
INHERITING FROM zclass_inheritance
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
METHODS public_method REDEFINITION .
METHODS sub_public_method.
PROTECTED SECTION.
METHODS protected_method REDEFINITION .
PRIVATE SECTION.
METHODS:private_method.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS zclass_sub_inheritance IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD public_method.
WRITE:'Redefined Sub Class Public Method'.
WRITE: /.
super->public_method( ).
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD protected_method.
super->protected_method( ).
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD private_method.
WRITE:'Only Sub Class Private Method'.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD sub_public_method.
WRITE: 'Called from the SUB_PUBLIC_METHOD'.
WRITE: /.
* super->super_public_method( ).
WRITE: /.
super_public_method( ). "No 'Super' Keyword
WRITE: /.
me->private_method( ).
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Report zinheritance_pgm
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*&
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
REPORT zinheritance_pgm.
**Let us call Super Class public Method directly
*DATA(lr_super_class) = NEW zclass_inheritance( ).
*lr_super_class->public_method( ).
*WRITE:/.
*lr_super_class->super_public_method( ).
*Let us call Super Class public Method from Sub Class
*DATA(lr_sub_class) = NEW zclass_sub_inheritance( ).
*WRITE:/.
*lr_sub_class->public_method( ).
*WRITE:/.
*lr_sub_class->super_public_method( ).
*WRITE:/.
*lr_sub_class->sub_public_method( ).
*Now Let us call Sub Class public method using casting
*DATA(lr_super_class) = NEW zclass_inheritance( ).
*DATA(lr_sub_class) = NEW zclass_sub_inheritance( ).
**Narrowing Caste
*lr_super_class = lr_sub_class.
*WRITE:/.
*lr_super_class->public_method( ).
*Let us call Super Class Public Method using casting
DATA(lr_super_class) = NEW zclass_inheritance( ).
DATA(lr_sub_class) = NEW zclass_sub_inheritance( ).
**Narrowing Caste
lr_super_class = lr_sub_class.
*Widening Casting
lr_sub_class ?= lr_super_class.
WRITE:/.
lr_sub_class->super_public_method( ).














Comments
Post a Comment