Working with Interfaces
Introduction:
- We will cover the following basic concepts:
- Basic differences between Classes and Interfaces.
- Creating Global Interface & Class in SE24.
- Call Interface Methods in the SE38 program.
- Basic differences between Interface Methods and Normal Methods.
- Bonus Point.
Lets Start:
- So what is this 'Interface'?
- Let us understand it by comparing it with Class as both are created in SE24 with the same screen layout.
 |
| Interface VS Class |
2. Create an Interface in SE24.
- Let us create an Interface with the name 'ZGLOBAL_INTERFACE'. Click on Create button.
- Select the 'Interface' radio button. Click on ok.
- Enter description as shown below. Click on save
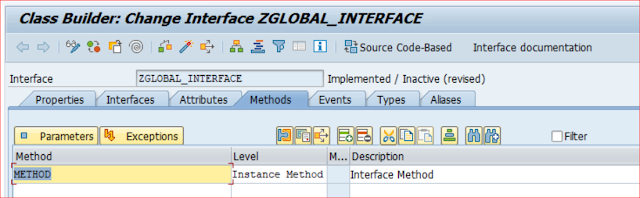
- Create Method Definition as shown below.
- Note here that the implementation part does not exist.
- Also, note that there is no Private and Protected Section in the Interface and yes that is interesting.
- Save and Activate the Interface.
- Now let us create 2 Global Classes and Implement the Created Interface in both.
- Create a Class in SE24 Tcode.
- Select Class Radio Button, Enter Description and Save.
- In the Interface tab of the Class, Let us declare the Interface ZGLOBAL_INTERFACE.
- Now Method of the interface is shown in the Methods Tab of Class.
- Interface Method Implementation Name: ZGLOBAL_INTERFACE~METHOD.
- As we can see, the Visibility of the Method is Public and we are not allowed to change it.
- Now let us Implement the Interface Method.
- Save, Check and Activate the Method & Class 1.
- Similarly, Create Class 2, Implement the Interface Method, Save, Check & Activate.
 |
| Create Class 2 |
 |
| Declare the Interface |
 |
| Create Class 2 Interface Method Implementation. |
3. Now let us call the Interface Methods in SE38 Program.
- Create an Executable Program in SE38.
- Call Interface Method using Class Reference Object.
- Create Object, Call Method using Object Component Selector ( -> ).
- But, we will get an error as shown below.
- This happens because the method is directly not available from the class.
- The Method is Inherited from Interface Definition.
- So let us call this method is a special way.
- Here, the trick is we have to call the method using interface ~Method( ) as shown below.
- Let us understand some basic differences between Normal Methods and Interface Methods.
- Similarly, let us call CLASS 2 Method as well.
4. There is another way for calling an interface method in a program.
- Let us create an Interface Reference Parameter instead of a Class Reference Parameter.
- As we see in the below example, while we create an object we use the type of the class of interest. In our case ZCLASS1 and ZCLASS2.
- And in this case we directly call the method Object->Method( ).
Sample Code:
REPORT zglobal_class_methods2.
*Let us Call Interface Methods From Class 1 & Class 2.
*Call the Method of Class 1
*Declare local variable with reference to the Class 1
DATA:lr_class1 TYPE REF TO zclass1.
*Create an object for the Class 1
CREATE OBJECT lr_class1.
*Call the Interface Method for the Class 1
lr_class1->zglobal_interface~method( ).
*Declare local variable with reference to the Class 2
DATA:lr_class2 TYPE REF TO zclass2.
*Create an object for the Class 2
CREATE OBJECT lr_class2.
*Cursor to Next Line
WRITE /.
*Call the Interface Method for the Class 1
lr_class2->zglobal_interface~method( ).
*Create Interface Reference Variable
DATA lr_interface TYPE REF TO zglobal_interface.
*Create Object for Interface Variable for Class 1.
CREATE OBJECT lr_interface TYPE zclass1.
*Cursor to Next Line
WRITE /.
*Call Interface Method
lr_interface->method( ).
*Create Object for Interface Variable for Class 2.
CREATE OBJECT lr_interface TYPE zclass2.
*Cursor to Next Line
WRITE /.
*Call Interface Method
lr_interface->method( ).
Note:
- If you like what you see, visit my blog on ABAP Workflow For Beginners.


















Comments
Post a Comment